node-red-contrib-generic-ble 4.0.3
Node-RED nodes for generic BLE devices
node-red-contrib-generic-ble
A Node-RED node set for providing access to generic BLE peripheral GATT characteristics.
As of v4.0.0, this node is optmized for Linux with BlueZ 5 D-Bus API (HCI socket is no longer used on Linux). The node should still work on macOS and Windows as nothing is modified for these platforms.
Supported operations are as follows:
- Start BLE Scanning
- Stop BLE Scanning
- Restart BLE Scanning (Stop then start BLE Scanning again)
- Connect to a peripheral device
- Disonnect from a peripheral device
- Read
- Write
- Write without Response
- Notify (Subscribing the Notify events)
The node status modes are as follows:
missingthe configured BLE peripheral device is missing. When the device is discovered, the state transitions todisconnected. Thedisconnecteddevice may transiton tomissingagain when RSSI is invalidated (Linux only)disconnectedwhen the configured BLE peripheral device is found but not connctedconnectingwhen the configured BLE peripheral device is being connectedconnectedwhen the configured BLE peripheral device is connecteddisconnectingwhen the configured BLE peripheral device is being disconnectederrorwhen unexpected error occurs
Known issues for Linux BlueZ D-Bus API:
- Unlike the older version, you must set the process owner's permission properly and manually. Non-root user's Node-RED process will fail to get this node working. Read
Installation Note (Linux)below. - It seems the local name in advertisement packet isn't transferred to
LocalNameproperty in org.bluez.Device1 BlueZ D-Bus API. With the HCI socket implementaion, the local name was resolved. So the local name can be resolved on macOS and Windows. Bluetooth: hci0: hardware error 0x03error sometimes occurs (and logged in syslog). When it's observed, all devices are disconnected and cahches are gone. The node tries to power on the BLE adapter again.
How to use
How to configure a new BLE peripheral device
At first, drag either a Generic BLE in node or a Generic BLE out node to the workspace from the node palette and double-click the node. And you can find the following dialog. Here, click the pencil icon (1) to add a new BLE peripheral or edit the existing one.
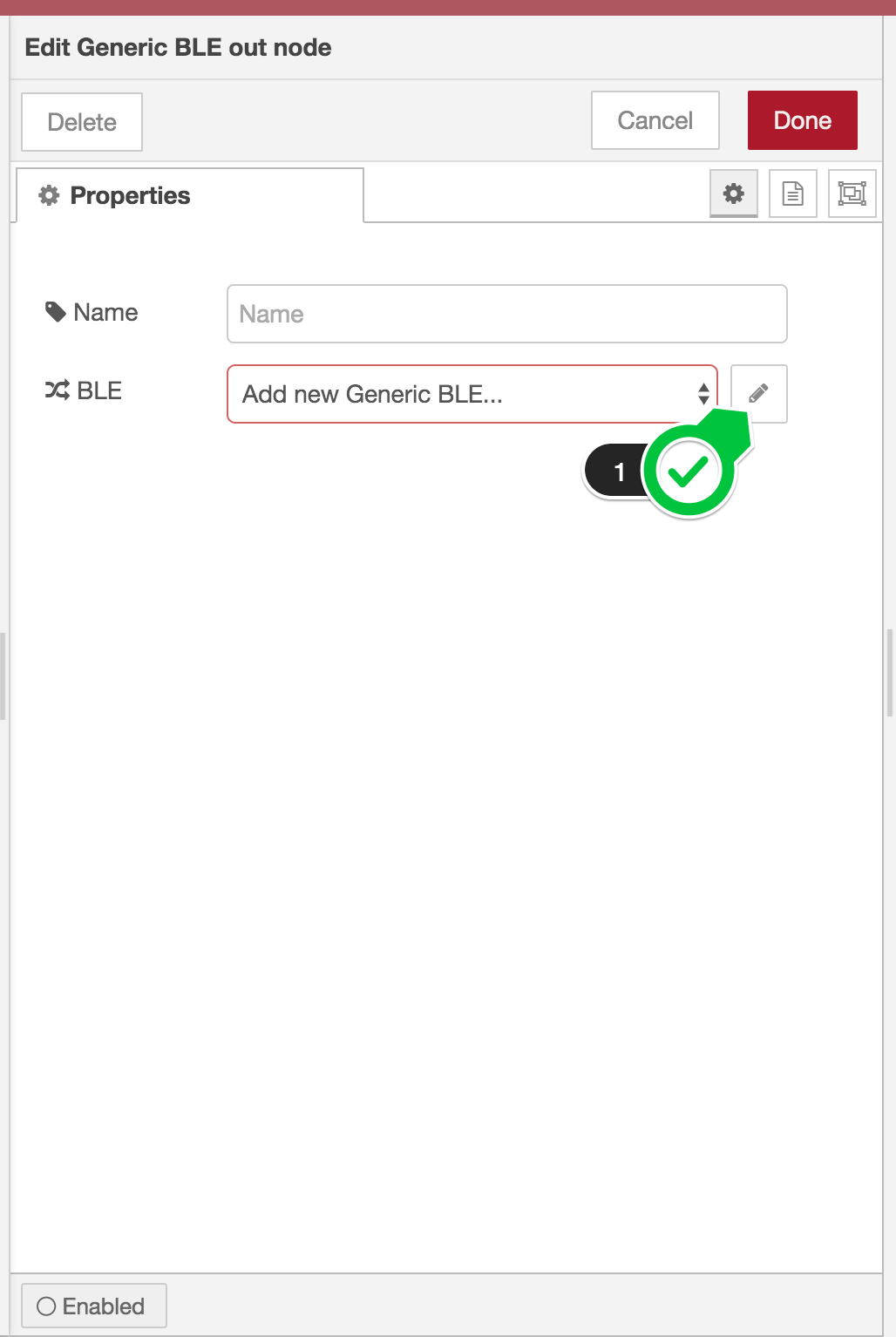
Then the new config node dialog appears as shown below.
The BLE Scanning shows whether or not BLE scanning is going on. In order to start BLE scanning, check it (2).
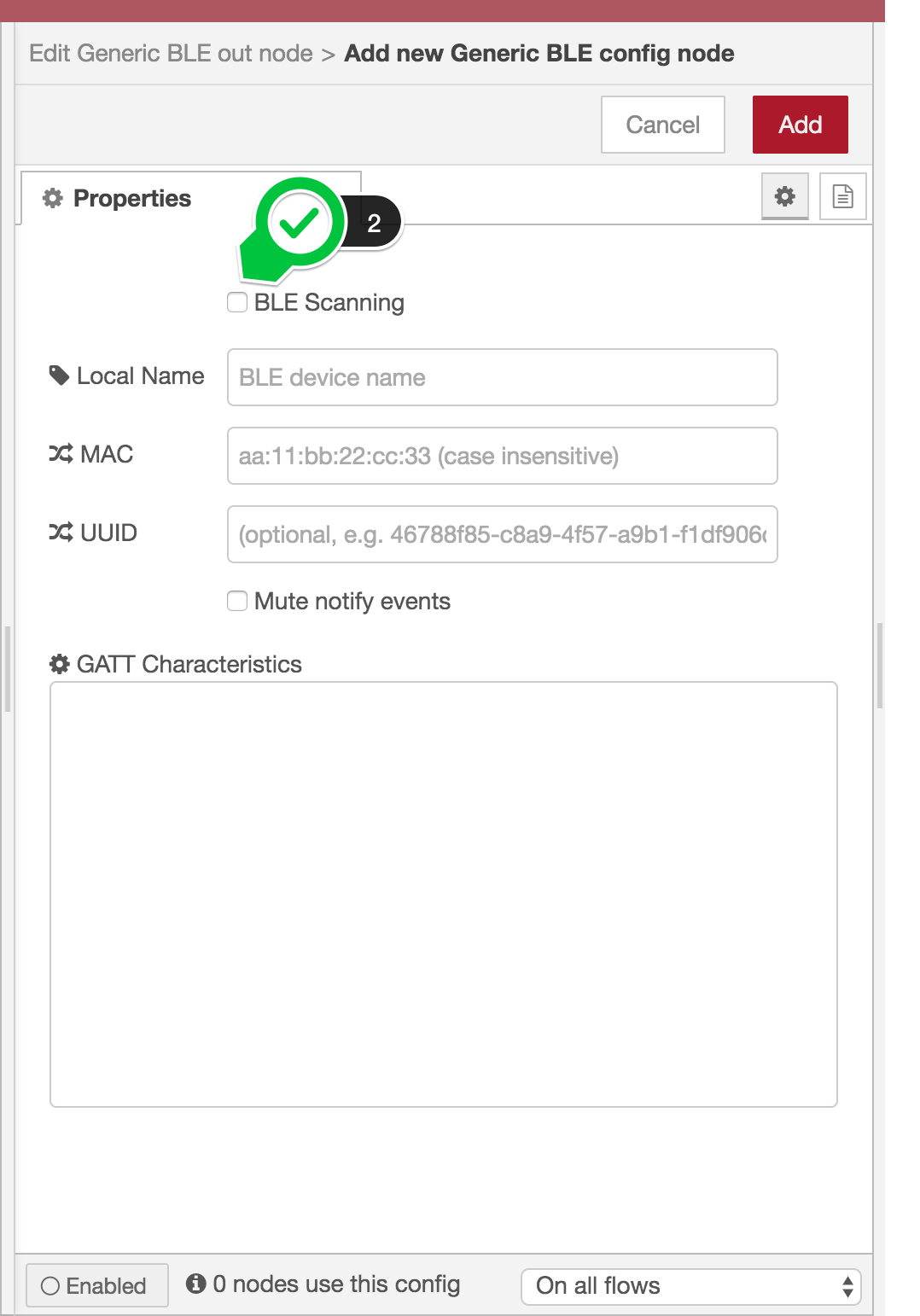
As soon as you check it, Scan Result select box and Apply button appear. The scan results are automatically fufilled in the select box. The content will be refreshed every 10 seconds.
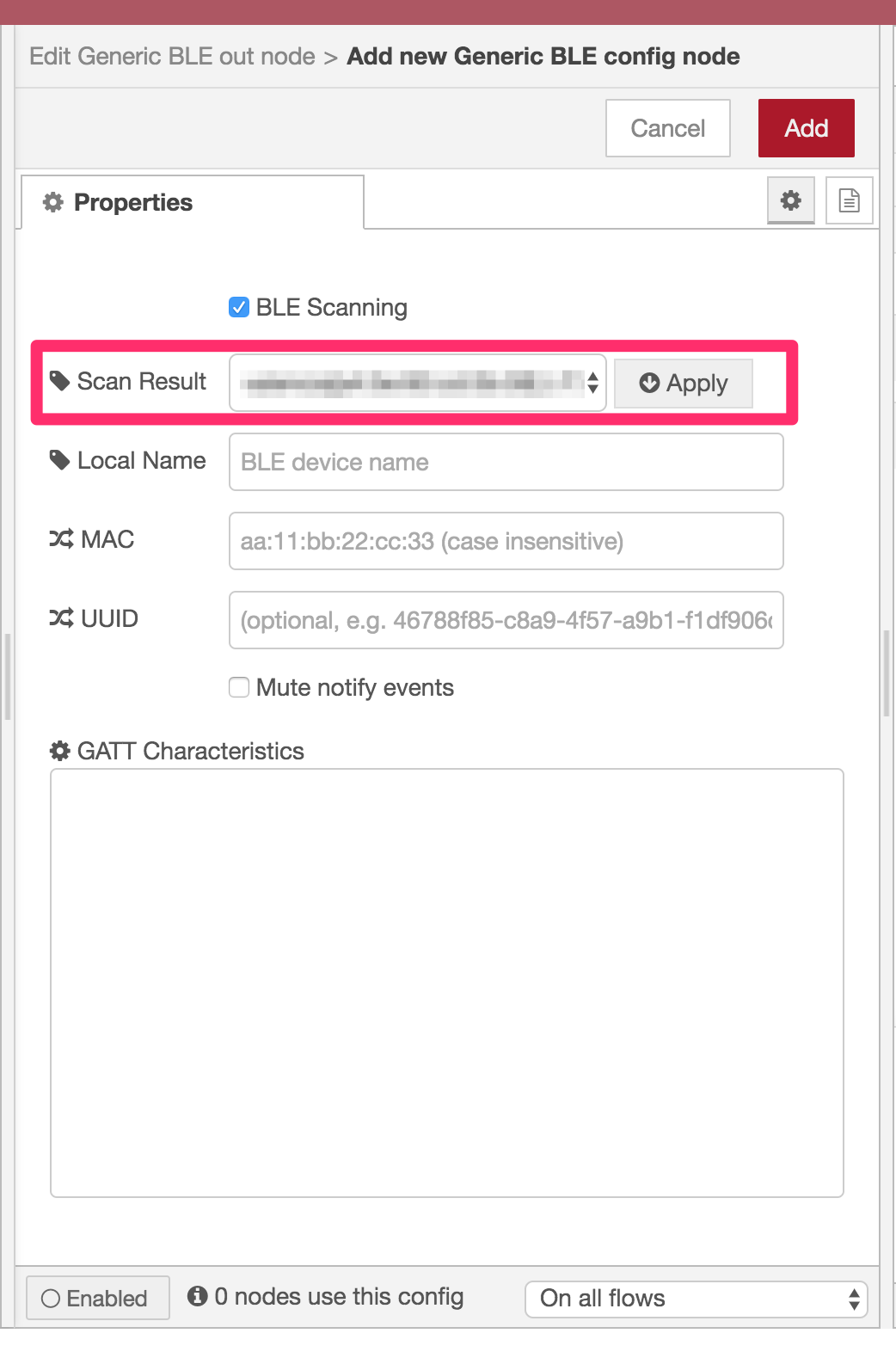
Chosoe one of the listed devices and then click Apply to populate Local Name, MAC and UUID input text boxes. Clicking Apply button also triggers GATT characteristics discovery as well.
The following picure shows the Apply button clicking results. GATT Characteristics has a characteristic list of the selected device. When you see (not available) message in the box, check if the device is NOT sleeping (a sleeping device fails to respond to a connect request) and click Apply again.
GATT Characteristics must be populated as the node uses the list to verify if a given characteristic UUID is valid on performing Read, Write and Subscribe requests.
Click Add (3) to save the information when everything is OK.
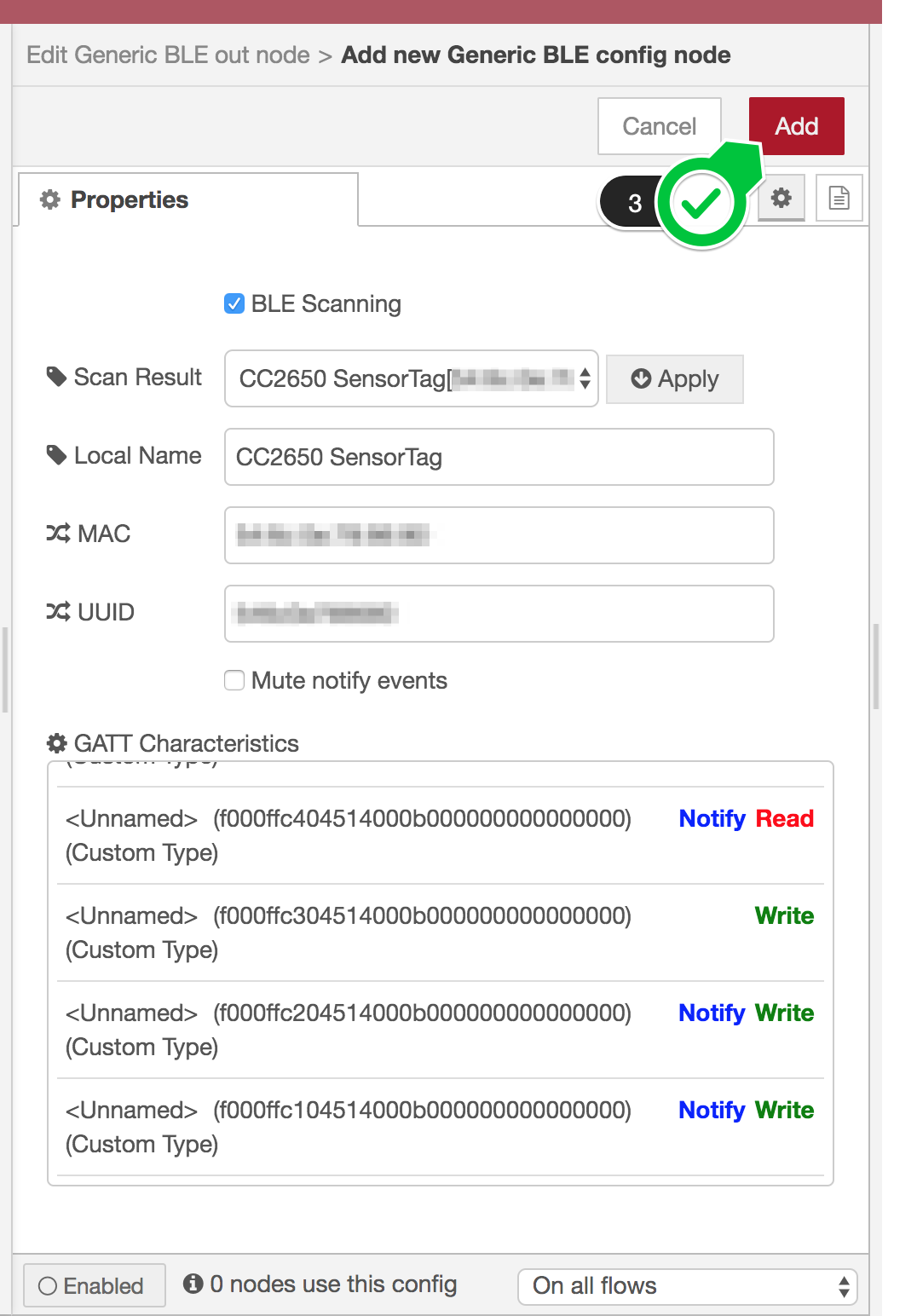
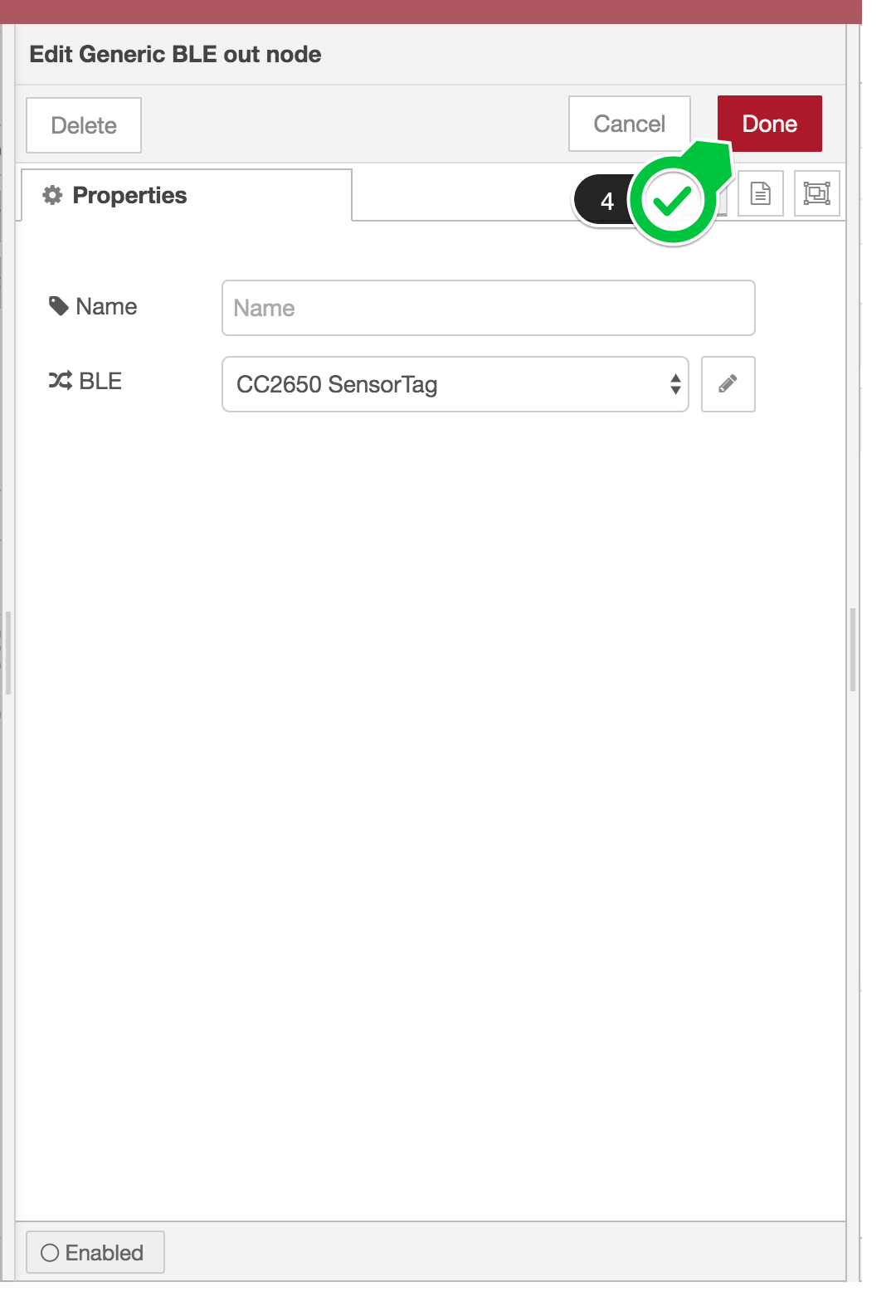
Now back to Generic BLE out node.
Click Done (4) to finish the Generic BLE out node settings.
You can also import an example flow from the menu icon(三) > Import > Examples > node-red-contrib-generic-ble > 01-read-write for learning more about this node.
How to translate gatttool command into flow
In this example, we show how to describe gatttool commands for characteristic value write and read with Generic BLE nodes.
NOTICE: As of BlueZ 5, gatttool is deprecated. gatttool will be removed in the future relesase.
Characteristics Value Write
The following simple command line just issues a characteristic write request to the handle 0x0027, which the BLE peripheral associates with the characteristic uuid f000aa02-0451-4000-b000-000000000000(uuids and handles can be listed by gatttool -b 88:99:00:00:FF:FF --characteristics command).
$ gatttool -b 88:99:00:00:FF:FF --char-write-req --handle=0x0027 --value=ca
Characteristic value was written successfully
In this tutorial, we translate the above command into Node-RED flow.
First of all, we use the following nodes.
injectnode to trigger a write requestGeneric BLE outnode to perform the write request
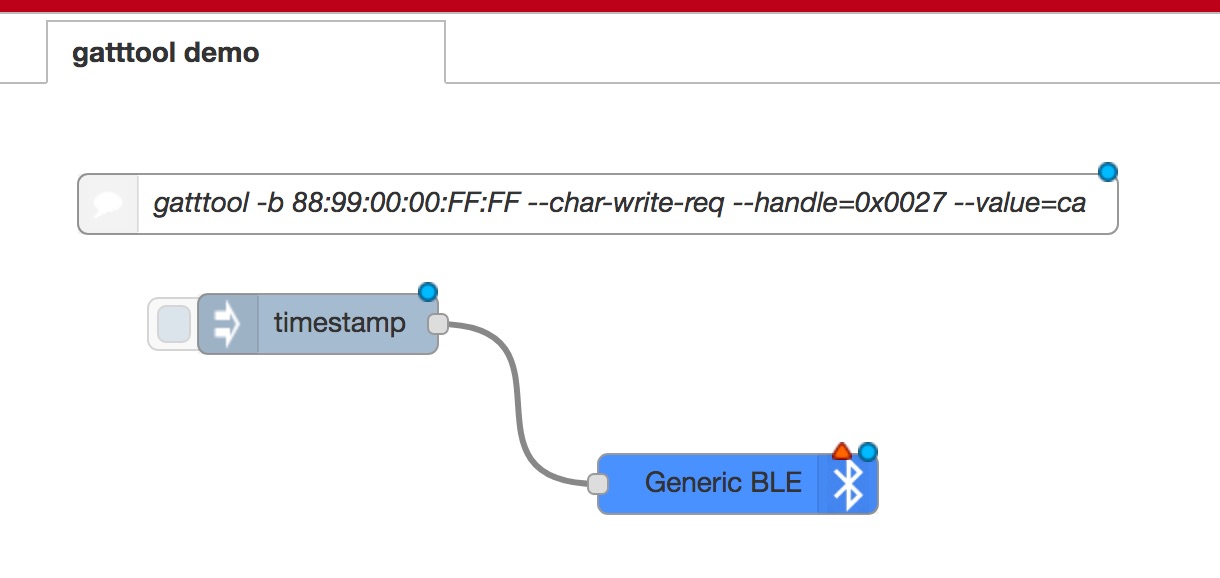
So the first step to create a flow is to place the above nodes on the workspace and connect them as shown above.
Next, open the inject dialog so that you can provide the write request parameters, the characteristic uuid and the value.
Important!) Unlike gatttool, Generic BLE nodes NEVER use handles. Always use uuids instead.
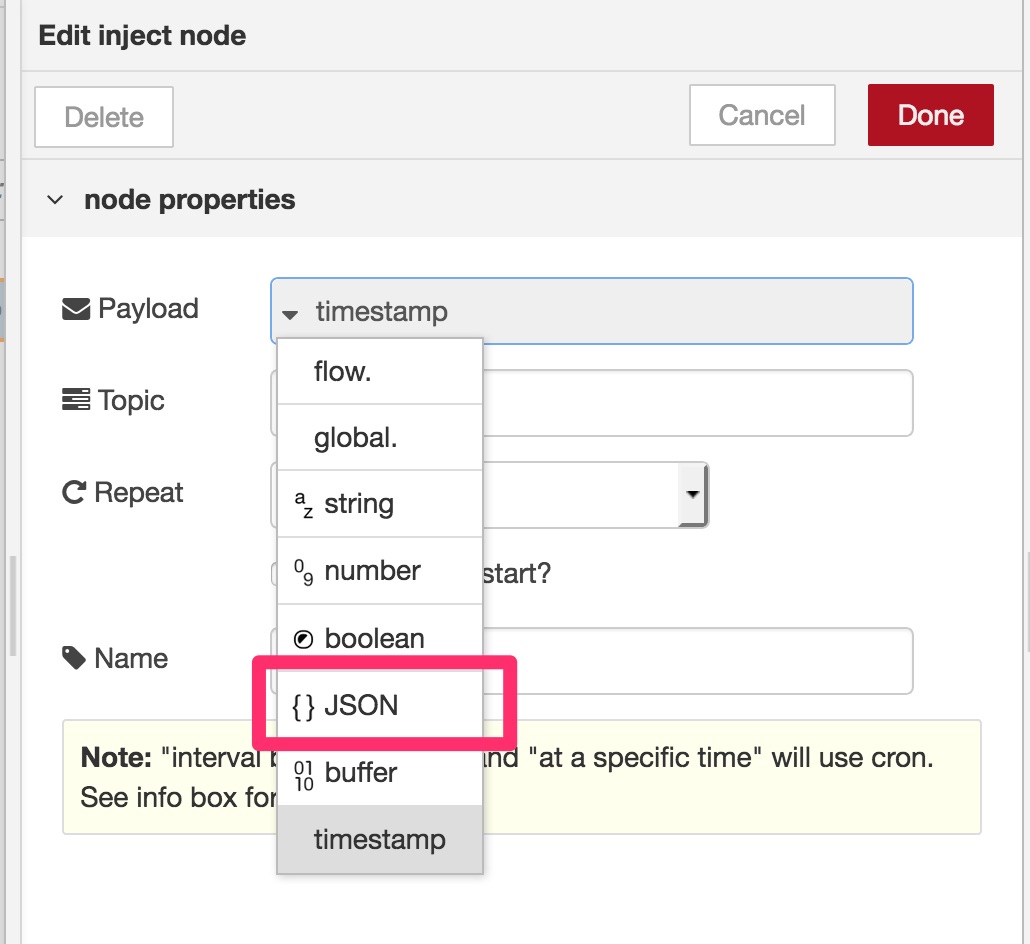
In this dialog, choose JSON at Payload input item since Generic BLE out node accepts a JSON object as its input value. See Inputs in the node description shown in the info tab for detail.
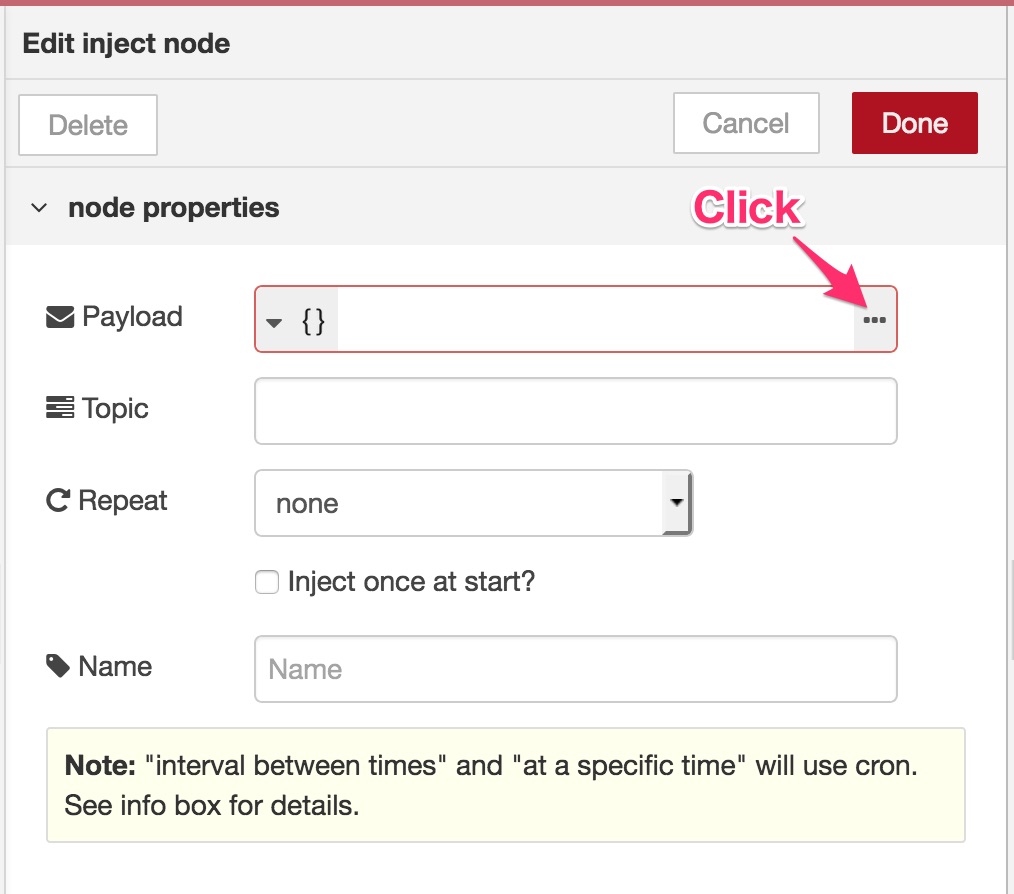
Click/tap ... to launch JSON value editor and populate the following JSON text.
{
"f000aa0204514000b000000000000000": "ca"
}
The property f000aa0204514000b000000000000000 is a characteristic uuid. However, unlike gatttool, you must strip hyphens from the original uuid value. Generic BLE nodes doesn't accept gatttool style uuid format.
The value ca is a hex string to be written, which is identical to the above command line.
So you'll see the following image.
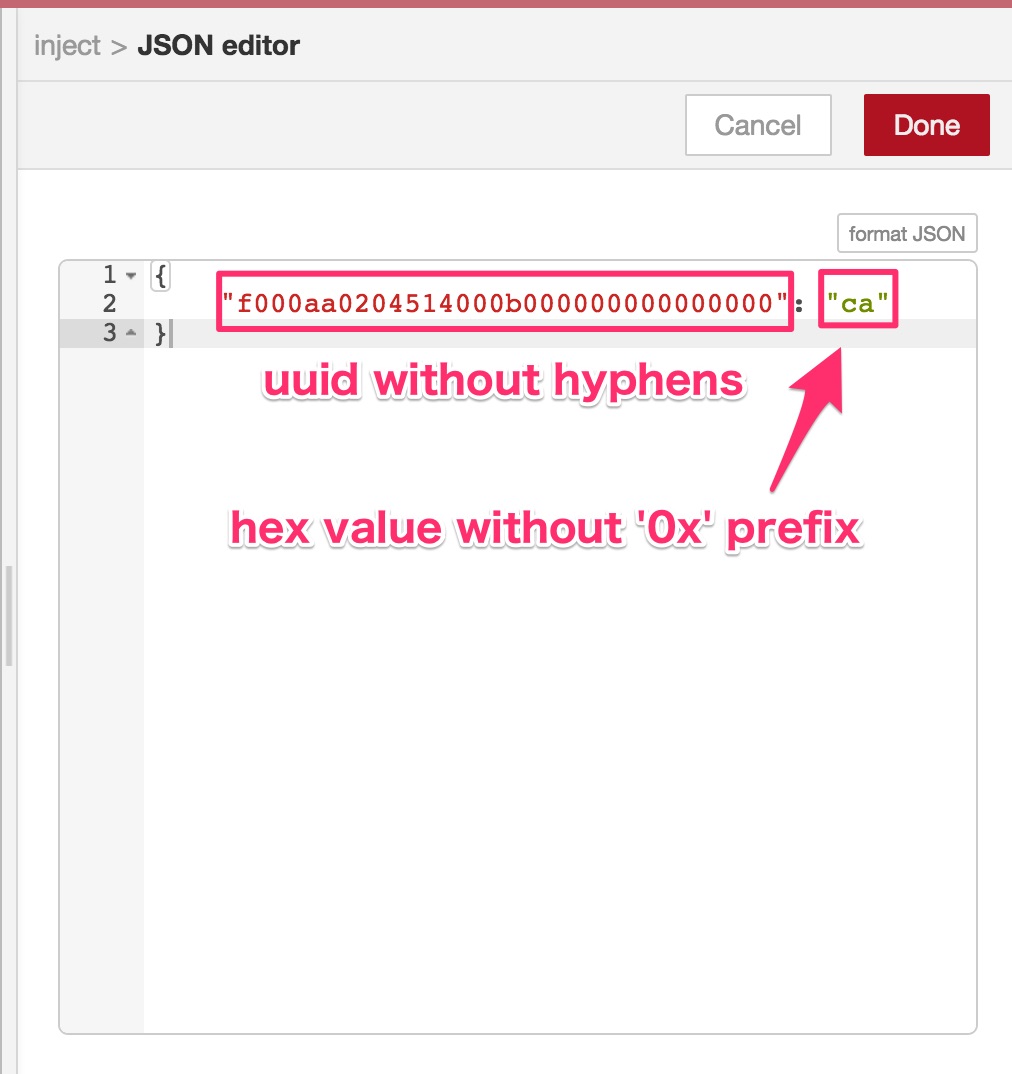
Close the dialog by clicking Done button after entering the JSON text.
Configure Generic BLE out node for your BLE peripheral (This step is already introduced above so we don't describe here. See How to configure a new BLE peripheral).
Now you're ready to issue a characteristic write request to your BLE peripheral. Click Deploy and click inject node to issue a characteristic write request.
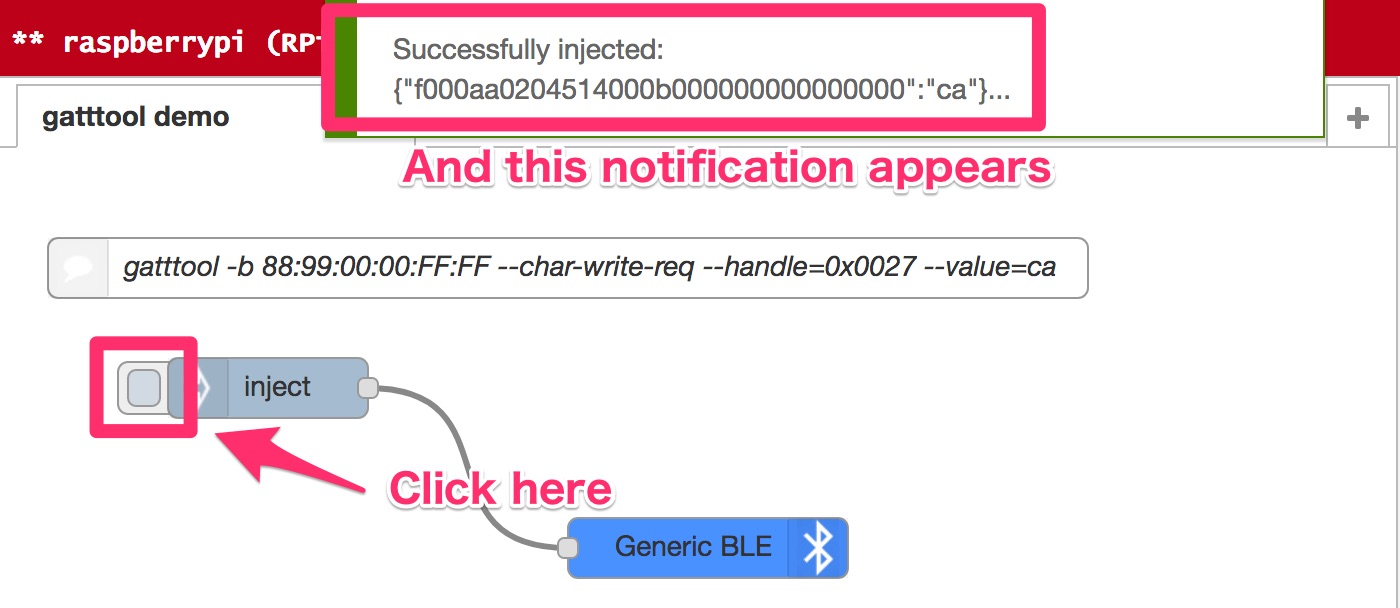
Node-RED shows the notification message after your write request is performed successfully.
Here in this tutorial, we use inject node to create characteristic write request parameters. However, this isn't the only way to do so. You can use other nodes than inject node. All you need is to prepare a valid JSON object for Generic BLE out node and provide it to the node.
In order to retrieve the written value from your BLE peripheral, go to the next step.
Characteristics Value Read
The both commands perform characteristic value read commands and return the same result, the characteristic value of the uuid f000aa02-0451-4000-b000-000000000000.
$ gatttool -b 88:99:00:00:FF:FF --char-read -u f000aa02-0451-4000-b000-000000000000
handle: 0x0027 value: ca
$ gatttool -b 88:99:00:00:FF:FF --char-read --handle=0x0027
Characteristic value/descriptor: ca
In this tutorial, we translate the above commands into Node-RED flow.
We use the following nodes this time.
injectnode to trigger a read commandGeneric BLE innode to perform the read commanddebugnode to show the read value
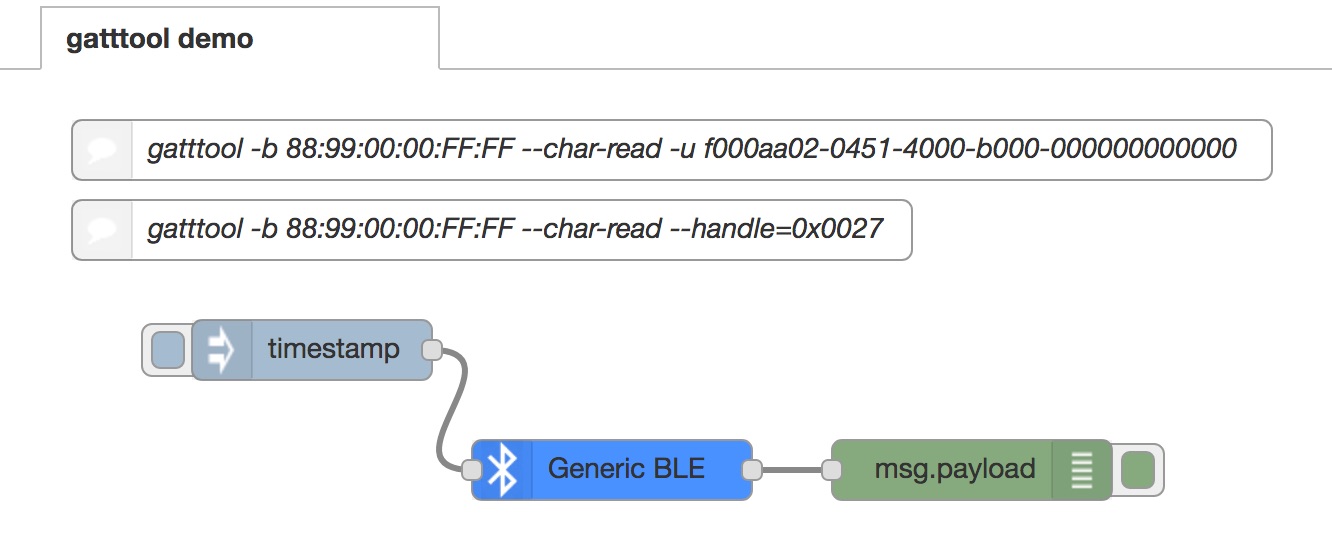
Put the above nodes onto your workspace and add connectors like above.
Open inject node dialog and enter the characteristic uuid at Topic input box. Leave default values other than Topic since Generic BLE in sees only the topic value.
You can also leave Topic empty when you want to retrieve all characteristics values.
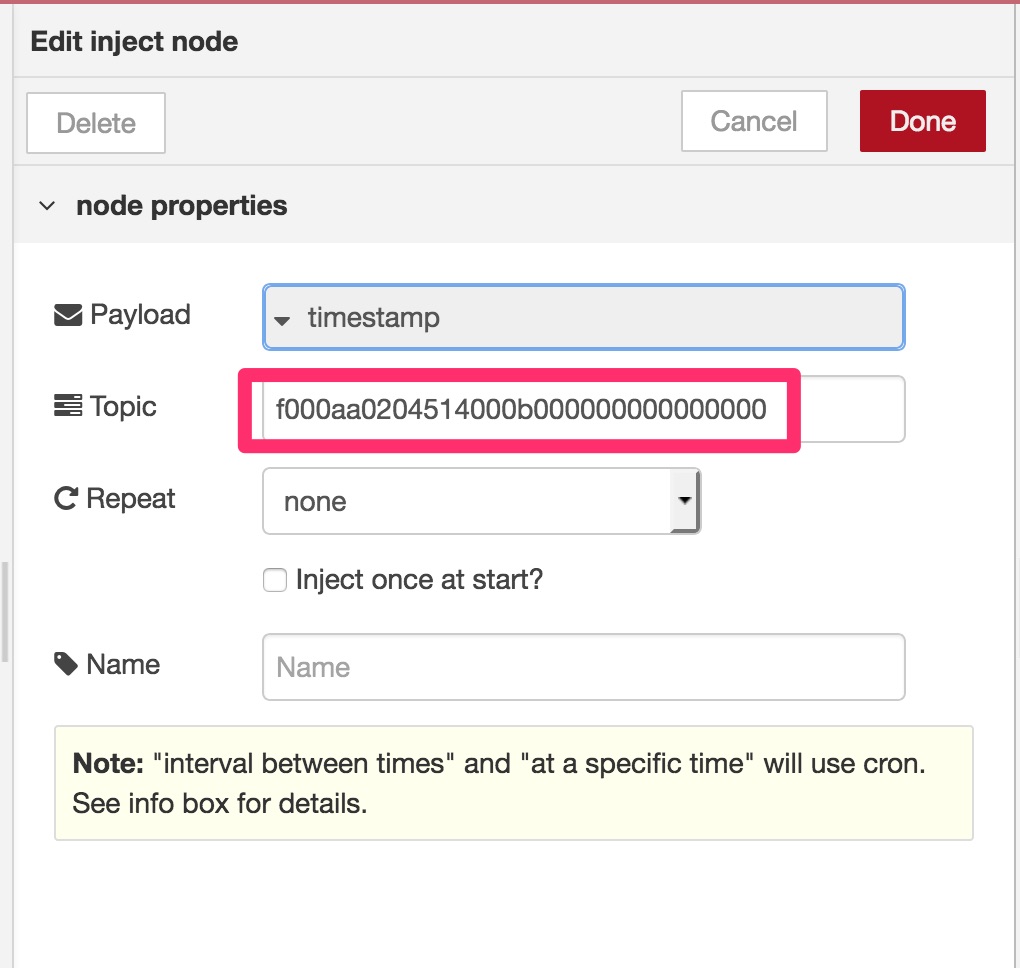
Click Done after entering the uuid to close the dialog. You need to configure Generic BLE in node to use your BLE peripheral but we skip to mention here as the instruction is described above (See How to configure a new BLE peripheral for detail).
Click Deploy to function the flow.
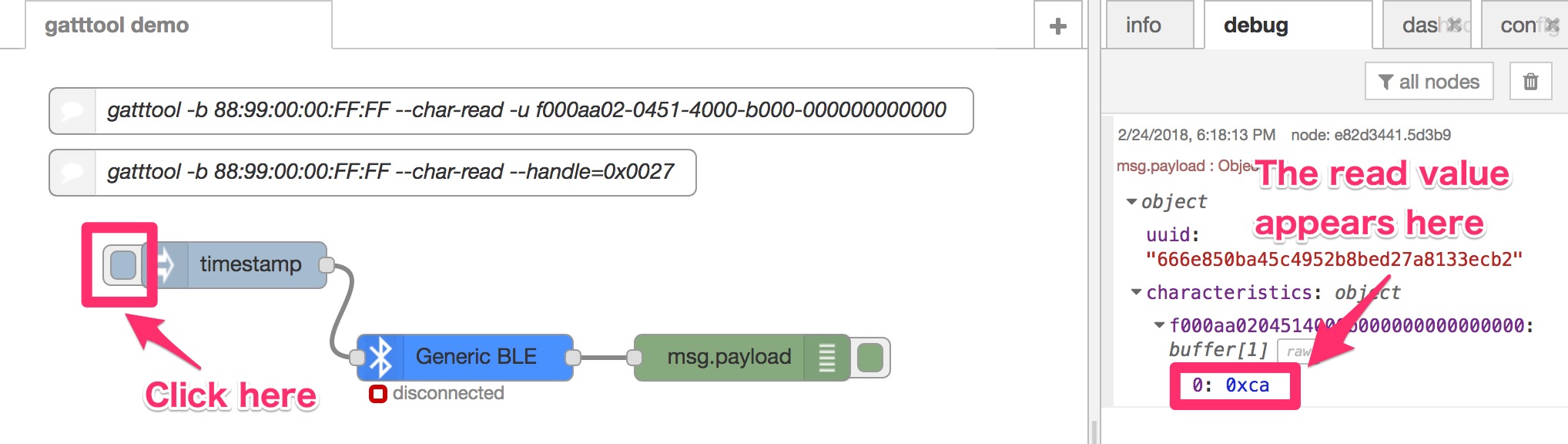
Let's read the characteristic value by clicking inject node pedal. The read result will be displayed on the debug tab.
BLE in and out nodes
See info tab for detail on the editor UI.
Example Flow
You can import the example flow on Node-RED UI.
Installation Note (Linux)
The Node-RED process owner must belong to bluetooth group in order to access BlueZ D-Bus API, otherwise this node doesn't work at all because of bluetoothd permission issue.
For example, if you're going to run the process by pi user, run the following command.
sudo usermod -G bluetooth -a pi
Then reboot the OS so that the policy changes take effect.
sudo reboot
Node-RED users
Run the following commands:
cd ~/.node-red
npm install node-red-contrib-generic-ble
Then restart Node-RED process. Again, for Linux users, read the above chapter Installation Note (Linux) to get this node working.
CANDY RED users
Run the following commands:
cd $(npm -g root)/candy-red
sudo npm install --unsafe-perm node-red-contrib-generic-ble
Then restart candy-red service.
sudo systemctl restart candy-red
Appendix
How to build
# build
$ NODE_ENV=development npm run build
# package
$ NODE_ENV=development npm pack

