node-red-contrib-ai-agent 0.5.1
AI Agent for Node-RED
Node-RED AI Agent
Note: This project is currently in beta and under active development. It is not yet stable, and many changes are expected. Use in production with caution.
Overview
A powerful AI Agent for Node-RED that enables natural language processing with memory and tool integration. This package provides nodes for creating AI-powered flows with conversation context management and extensible tool integration.
⚠️ Beta Notice
This project is currently in beta and under active development. Please be aware that:
- Breaking changes may occur between releases
- Not all features are fully implemented or stable
- Documentation may be incomplete
- Performance optimizations are still in progress
Your feedback and contributions are highly appreciated!
Features
- AI Agent Node: Process messages with AI, maintaining conversation context
- AI Agent Orchestrator Node: Participates in orchestrated flows via Chain Discovery
- Memory Nodes:
- In-Memory: Store conversation context in memory (volatile)
- File-based: Persist conversation context to disk
- AI Model Node: Configure AI models and API settings
- AI Orchestrator Node: Coordinate multiple agents and create autonomous plans
- Tool Integration: Extend functionality with custom tools
- Stateless Design: Memory nodes are stateless, making them more reliable and scalable
- Context Management: Automatic conversation history management with configurable retention
Getting Started
- Install the package via the Node-RED palette manager
- Add an AI Model node to configure your OpenRouter API key and model
- (Optional) Add a Memory node (In-Memory or File-based) to manage conversation context
- (Optional) Add AI Tool nodes to define custom functions or HTTP requests
- Connect to an AI Agent node to process messages
- (Optional) Connect more AI Agent nodes to process messages in a chain
Example: Today's Joke
Here's an example flow that tells a joke related to today's date using a custom tool:
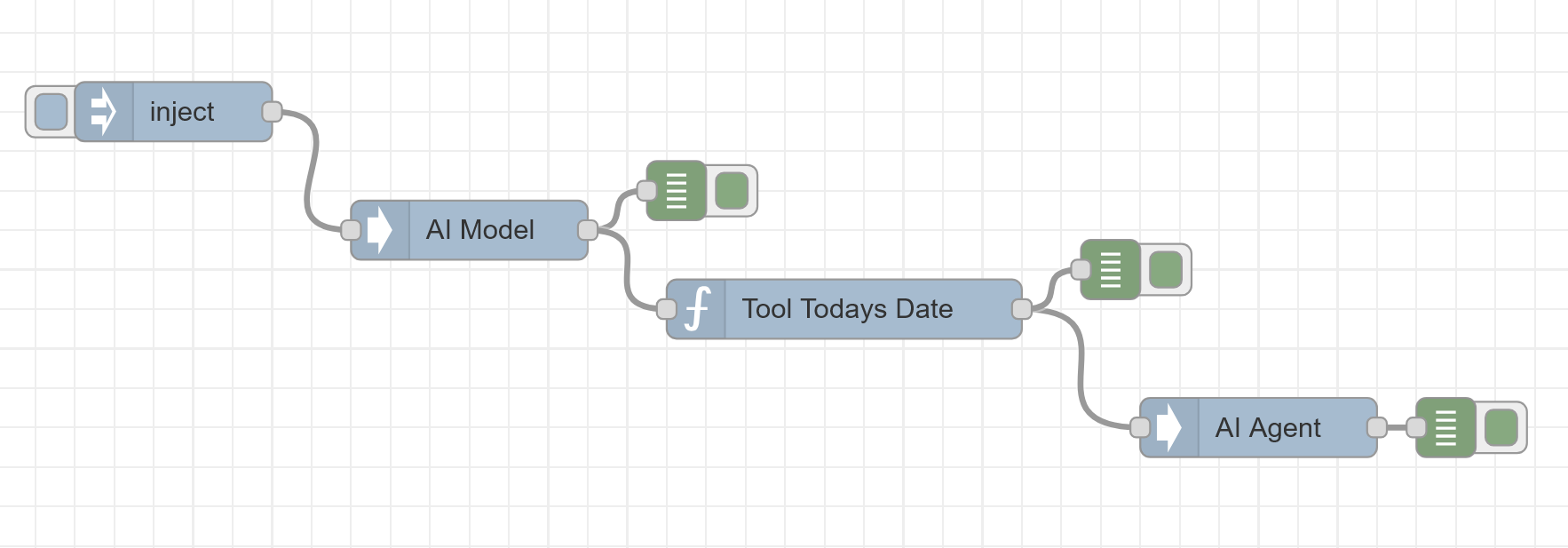
Flow Output
When executed, the flow will generate a joke related to the current date:

Node Types
AI Agent
Processes messages using the configured AI model and maintains conversation context through connected memory nodes.
Properties:
- Name: Display name for the node
- System Prompt: Initial instructions for the AI
- Response Type: Format of the response (text or JSON object)
AI Agent Orchestrator
A specialized version of the AI Agent designed for multi-agent workflows. It "tags" messages in a pipeline so the AI Orchestrator can discover it.
Properties:
- Name: Display name for the node
- Capabilities: Comma-separated list of skills (e.g.,
coding, research) - System Prompt: Instructions for this specific expert
Memory (In-Memory)
A configuration node that initializes the conversation context in memory. The agent node uses this configuration to manage the conversation context.
Properties:
- Max Items: Maximum number of conversation turns to keep in memory
- Name: Display name for the node
Memory (File)
A configuration node that initializes the conversation context with file-based persistence. The agent node uses this configuration to manage the conversation context across restarts.
Properties:
- Filename: Path to store the memory file (relative to Node-RED user directory)
- Max Conversations: Maximum number of conversations to store
- Max Messages Per Conversation: Maximum messages per conversation history
- Backups: Enable/disable automatic backups
- Backup Count: Number of backups to keep
- Consolidation: Threshold of messages to trigger auto-summarization
- Long-Term Memory: Enable/disable vector-based storage
- Embedding Model: The model used for semantic embeddings (e.g., text-embedding-ada-002)
- Name: Display name for the node
AI Model
Configures the AI model and API settings.
Properties:
- Model: The AI model to use (e.g., gpt-4, claude-3-opus)
- API Key: Your OpenRouter API key
- Name: Display name for the node
AI Orchestrator
Coordinates multiple AI agents by creating and executing plans. It uses Chain Discovery to identify available agents from its input message.
Key Features:
- Chain Discovery: Implicitly discovers agents wired in a pipeline before it.
- Zero-Wire Execution: Calls discovered agents directly via code (no messy routing wires).
- Non-linear Planning: Supports task dependencies (tasks wait for their predecessors).
- Error Recovery: Automatically handles task failures with recovery strategies.
Properties:
- Max Iterations: Maximum cycles for the autonomy loop
- Planning Strategy: Simple (linear) or Advanced (dependency-aware)
- Default Goal: Optional fallback goal
- Name: Display name for the node
AI Tool Function
Creates a JavaScript function tool that can be used by the AI Agent.
Properties:
- Name: Display name for the node
- Tool Name: Name of the tool (used by the AI to identify the tool)
- Description: Description of what the tool does
- Function: JavaScript code to execute when the tool is called
AI Tool HTTP
Creates an HTTP request tool that can be used by the AI Agent to make external API calls.
Properties:
- Name: Display name for the node
- Tool Name: Name of the tool (used by the AI to identify the tool)
- Description: Description of what the tool does
- Method: HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.)
- URL: The URL to make the request to (supports template variables)
- Headers: JSON object of headers to include in the request
- Body: Content to send in the request body
Example: https://api.example.com/users/${input.userId}
Template Variables: You can use template variables in the URL, headers, and body to reference properties from the input object that the AI provides when calling the tool.
AI Tool Approval
Creates an approval tool that can be used by the AI Agent to request human intervention. When called, the agent's execution pauses until a human provides a response.
Properties:
- Name: Display name for the node
- Tool Name: Name of the tool (used by the AI to identify the tool)
- Description: Description of what the tool does (e.g., "Request approval for payments")
Output 2 (Approval Request): Sends a message with msg.payload containing the human question and msg.approvalId to be used for the response.
Example: Basic Usage
Here's how to use the AI Agent:
- Add an AI Agent node to your flow
- Configure it with an AI Model node
- (Optional) Add a Memory configuration node if you need conversation context
- Connect your flow:
[Input] --> [AI Model] --> [AI Agent] --> [Output]
Memory is only required if you need to maintain conversation context between messages or chain multiple agents together. For simple, stateless interactions, you can use the AI Agent without any memory configuration.
Example: Using AI Tools
To extend the AI Agent with custom tools:
- Add an AI Tool Function or AI Tool HTTP node to your flow
- Configure the tool with appropriate settings
- Connect the tool to the AI Agent:
[Input] --> [AI Model] --> [AI Tool] --> [AI Agent] --> [Output]
The AI Agent will automatically detect and use the tools in its processing. You can add multiple tools to give the AI Agent different capabilities.
HTTP Tool Example
[AI Tool HTTP] --> |
|--> [AI Agent] --> [Output]
[AI Tool Function] --> |
In this example, the AI Agent has access to both an HTTP tool for making external API calls and a function tool for custom logic.
Example: Chained Agents
For more complex scenarios, you can chain multiple agents to process messages in sequence:
- Create Memory node (it will init the context, it will be shared between agents)
- Configure Agent 1
- Configure Agent 2
- Connect your flow:
[Input] --> [AI Model] --> [AI Memory] --> [Agent 1] --> [Agent 2] --> [Output]
Each agent will maintain its own conversation context based on its memory configuration.
Example: Autonomous Orchestration (Chain Discovery)
The AI Orchestrator can manage complex, multi-step tasks by utilizing specialized agents in a pipeline:
- Add an AI Orchestrator node.
- Add one or more AI Agent Orchestrator nodes (e.g., "Coder", "Researcher").
- Connect them in a line:
[Inject Goal] --> [Coder] --> [Researcher] --> [Orchestrator] --> [Debug]. - The Orchestrator will automatically discover the "Coder" and "Researcher" via the message pipeline and call them as needed to achieve the goal.
This linear architecture keeps your flows clean while allowing for powerful, multi-agent collaboration.
Best Practices
Memory Management
- Memory nodes are configuration nodes that define how conversation context is managed
- Each AI Agent node references a memory configuration
- The memory configuration is instantiated once and can be shared between multiple agents
- The AI Agent node is responsible for managing and updating the conversation context based on its memory configuration
- Memory configurations are particularly useful in chained agent scenarios where different agents need different context handling
- Use In-Memory configuration for temporary conversations
- Use File-based configuration for conversations that should persist across restarts
- Set appropriate
maxItemsto control context length and memory usage
Error Handling
- Always handle errors from the AI Agent node
- Check for API key and model configuration errors
- Monitor memory usage with large conversation histories
Performance
- For high-volume applications, consider using a database-backed memory implementation
- Be mindful of token usage with large contexts
- Use appropriate timeouts for API calls
Advanced: Chaining Agents
You can chain multiple AI Agents with different memory scopes to create complex conversation flows:
[Input] -->[Memory 1] --> [Agent 1] --> [Agent 2] --> [Memory 2] --> [Agent 3] --> [Agent 4] --> [Output]
This allows for complex conversation flows where different agents handle different aspects of the interaction.
Advanced Features
1. Vector Storage (Long-Term Memory)
The AI Memory (File) node supports vector-based storage. When enabled, it can store embeddings of summaries or key information. This allows for semantic search using the query command.
2. Memory Consolidation
Automatically (or manually) summarize conversation threads to save space and maintain long-term context. After a threshold of messages is reached, the node can use an AI model to summarize the history and store it in the vector database.
3. Memory Commands
Memory nodes support the following commands via msg.command:
- add: Add a message to a conversation (
msg.messagerequired). - get: Retrieve messages for a conversation (
msg.conversationIdoptional). - search: Plain-text search across conversations (
msg.queryrequired). - query: Semantic (vector) search in long-term memory (
msg.querytext or vector required). - consolidate: Manually trigger summarization and long-term storage.
- clear: Clear short-term, long-term, or all memory.
- delete: Delete a specific conversation (
msg.conversationIdrequired).
4. Template Variables
Use dynamic values in HTTP requests via ${input.property} syntax.
Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Whether you want to report bugs, suggest features, or submit code changes, please feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request.
How to Contribute
- Report bugs or suggest features by opening an issue
- Submit pull requests for bug fixes or new features
- Help improve documentation
- Test the package and report any issues you find
Reporting Issues
When reporting issues, please include:
- Node-RED version
- Package version
- Steps to reproduce the issue
- Any error messages received
Development
To contribute to development:
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Make your changes
- Submit a pull request
