@septentrio/node-red-sbf-mixer 1.0.4
Mix sbf file, serial input and receiver output

SbfMixer
A node-red plugin to parse, show, edit, and emulate Septentrio Receiver !
Installation
You need to install Sbf Parser to decode Sbf (Septentrio Binary Format) from the receiver.
pip install sbf-parser
You can now install SbfMixer by going to:
Menu > Manage Palette > Palette > Install > Search for "mixer" > Install @septentrio/node-red-sbf-mixer
You must also install node-red-node-serialport
Or directly with npm :
cd ~/.node-red
npm install @septentrio/node-red-sbf-mixer
npm install node-red-node-serialport
Et voila !
If you want a steps-by-steps tutorial on SbfMixer, you can check tutorial.md
Examples
Release note
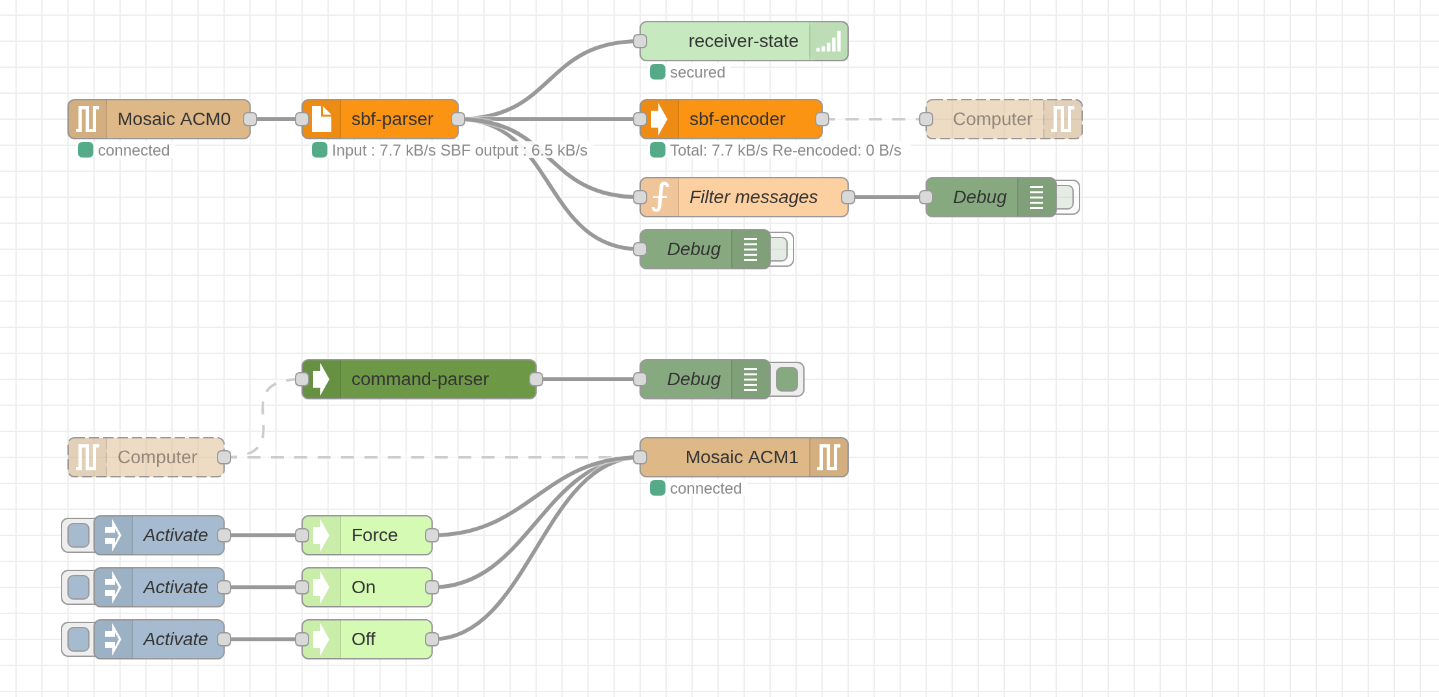
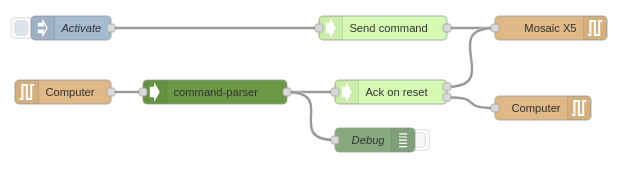
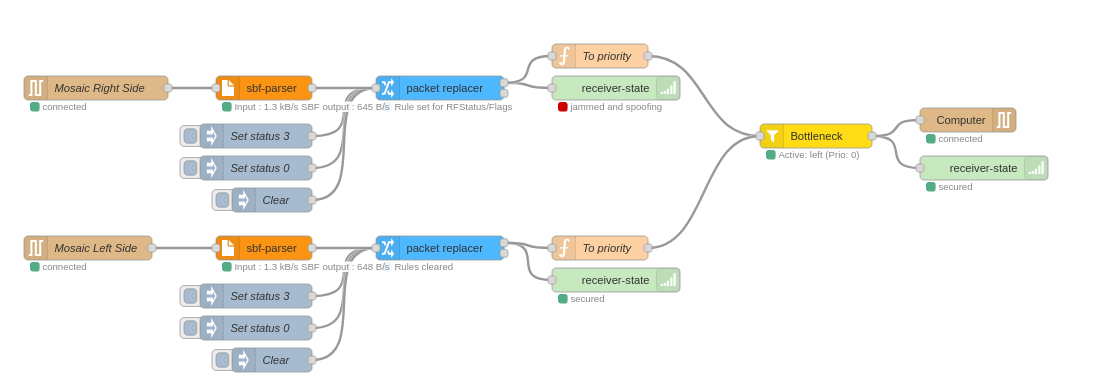
This package contains these nodes :
Working with Sbf stream :
sbf_parser: Convert binary from serial to Sbf blocks. Each message will have apayloadargument containing the original binary of the message.sbf_encoder: Encode each Sbf message without payload and return binary buffer ready to be output to serial connection.command_parser: Parse command send by your computer using plain text encodingack_command: Simulate an acknowledgment from a virtual receiver.
Editing Sbf :
packet-replacer: Replace value of chosen blocksspoofing: Not yet released.player: Play sbf block received according to their TOW
Utils :
receiver-state: Show receiver jamming and spoofing statuson-change: Send sbf block when they differ from the last onebottleneck: Allow to choose from multiple Sbf input
Tutorial
Setup receiver
You can read SBF directly from mosaic by plugin it to your computer :
- Go to https://192.168.3.1/ to enable the output of some SBF messages
- Go to NMEA/SBF Out
- Click New SBF Stream
- Select USB Port
- Select USB1
- Choose your messages to output, for example, Status, PVTGeod and GAL
- Confirm with Ok
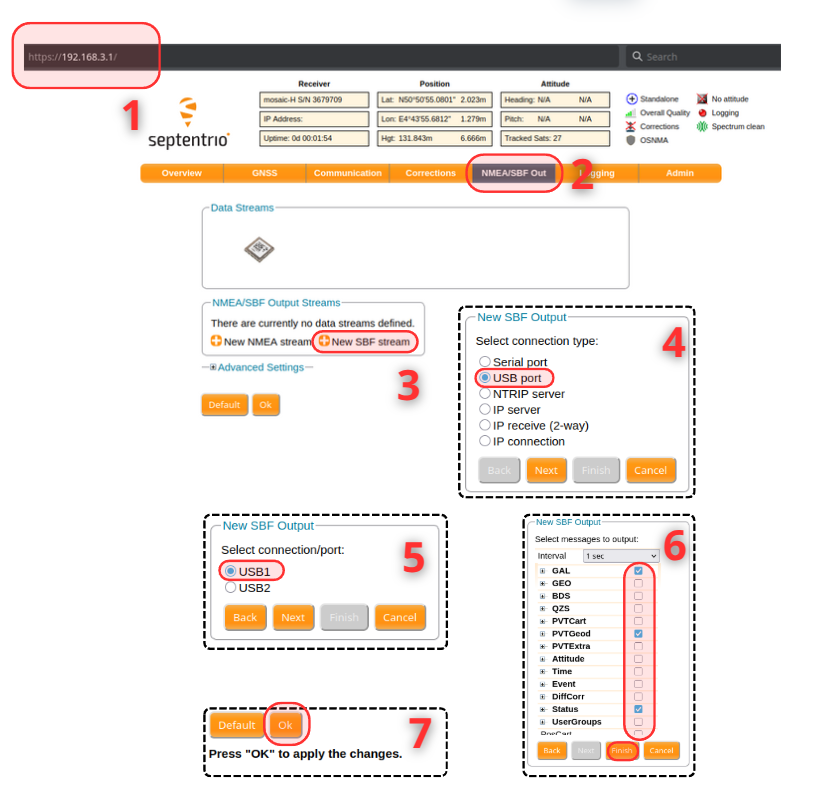
You should now have SBF stream to your computer, you can check by using cat /dev/ttyACM1 (could possibly be /dev/ttyACM0)
You can now configure your Serial block by giving it a name, an input stream (/dev/ttyACM1) and the baudrate (115200).
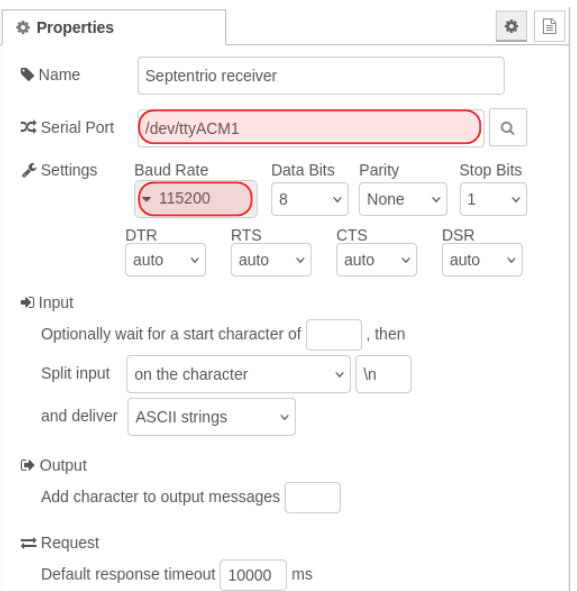
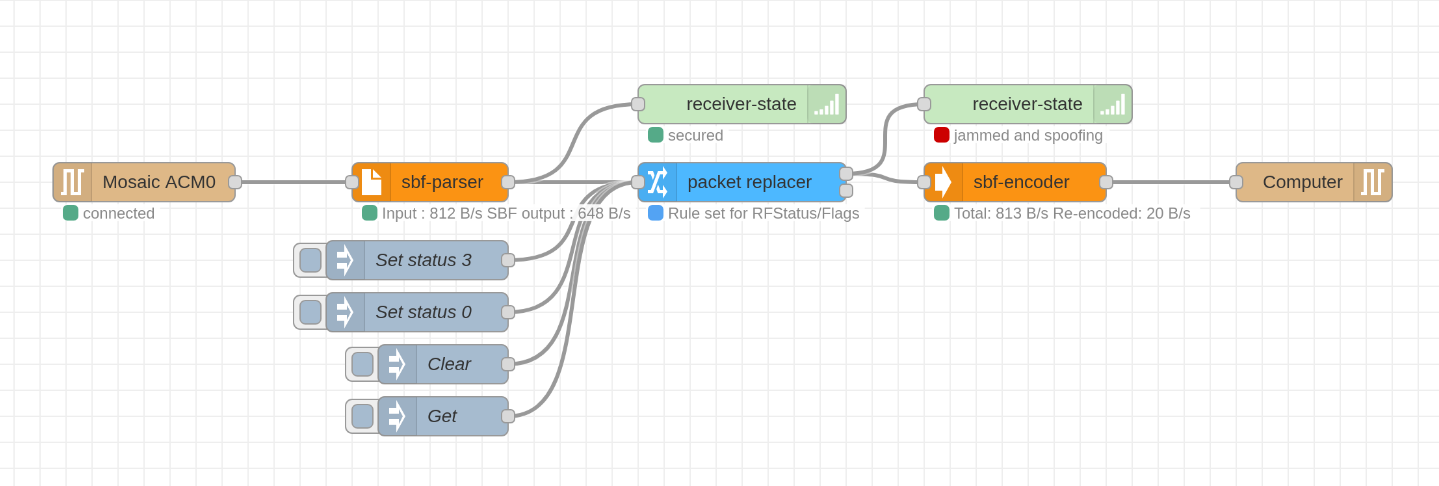
Sbf Parser
The incoming stream from the serial connection use buffer of bytes. To group and decode them, you should pass it to sbf-parser.
This block will send the binary to the Cython sbfParser and return the result in a Json message. For exemple with a ReceiverStatus message :
{
"type":"SBF",
"blockName":"ReceiverStatus",
"block":{
"blockName":"ReceiverStatus",
"blockType":"SBF",
"TOW":4294967295,
"WNc":65535,
"Temperature":141,
"CPULoad":17,
"RxError":8,
...
"N":4,
"AGCState":[
{"FrontendID":0,"Gain":49,"SampleVar":102,"BlankingStat":0},
{"FrontendID":1,"Gain":56,"SampleVar":102,"BlankingStat":0},
{"FrontendID":11,"Gain":59,"SampleVar":102,"BlankingStat":0},
{"FrontendID":3,"Gain":56,"SampleVar":96,"BlankingStat":0}
],
},
"payload":[36,64, ...],
"_parsed_by":"name_of_the_parser_used",
}
FAQ
How to output to an autopilot? (CubeOrange / Pixhawk / Other)
You may need a TTL cable to emulate a serial connection, like the Septentrio receiver does with /dev/ACM0.
After connecting your cable, you will see a new device, usually named /dev/ttyUSB0, which you can use just like the one for the Septentrio receiver via a serial block.
By default, these cables can echo each input they receive. This can lead to several issues when connecting two TTL cables (infinite echo) or when connecting to an autopilot. You can disable this behavior using:
stty -F /dev/ttyUSB0 -echo
Can I use Sbf-Mixer on the same computer as my drone emulator/pilot?
The recommended setup uses a dedicated Raspberry Pi or computer to run Sbf-Mixer separately:
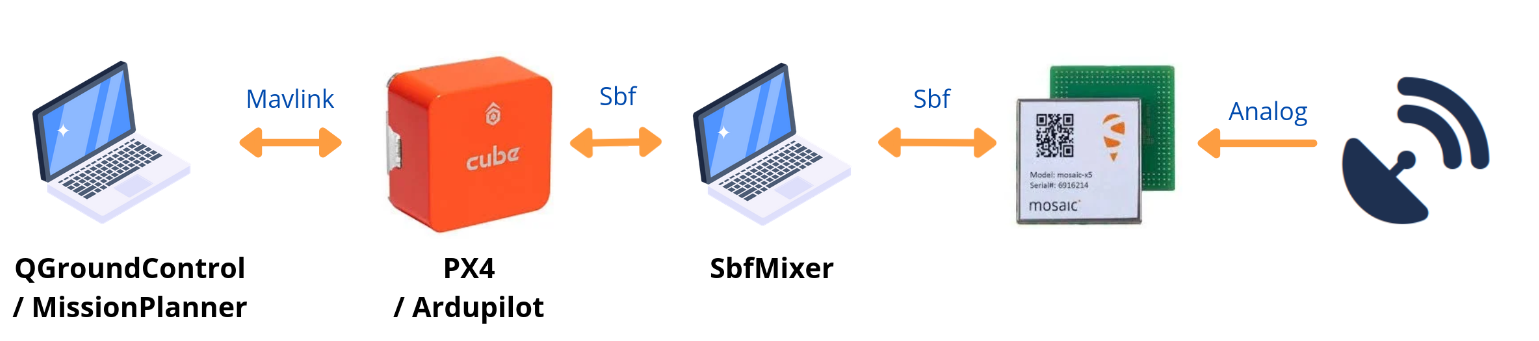
You may be able to use a setup like this one:
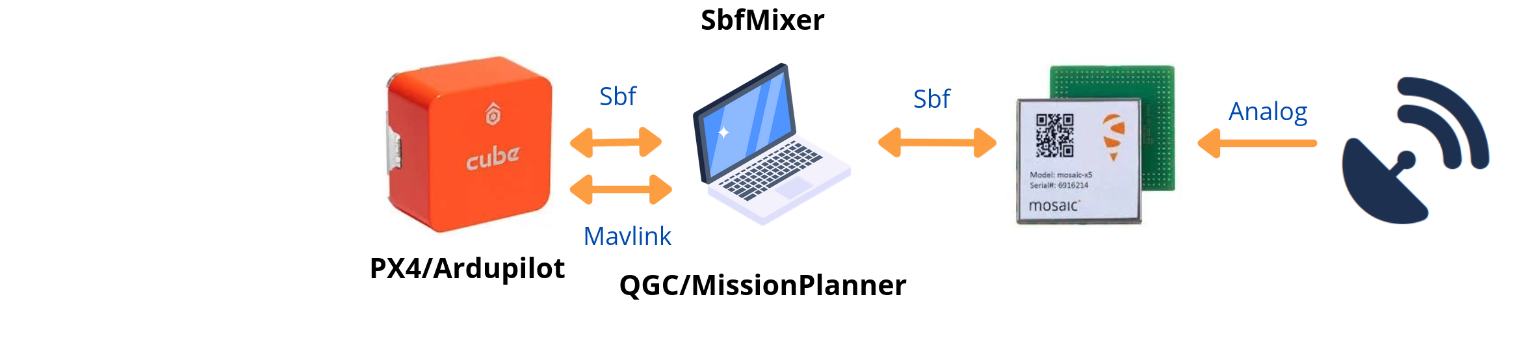
However, running QGC/MP on the same computer connected to the Mosaic will allow the ground control station to interact with the Septentrio receiver already used by the autopilot.
You can try to separate them by using Docker with: --device=/dev/ttyUSB0