@montagny/node-red-contrib-lorawan-bacnet 1.1.7
Custom Node-RED nodes to interface LoRaWAN devices with BACnet protocol.
LoRaBAC, an open-source LoRaWAN to BACnet interface
The LoRaBAC node is the configuration node of the LoRaBAC application.
1. Overview
1.1. What is LoRaBAC?
LoRaBAC is open-source application built on Node-RED. It allows you to integrate LoRaWAN devices with BACnet controllers, making it ideal for smart building applications.
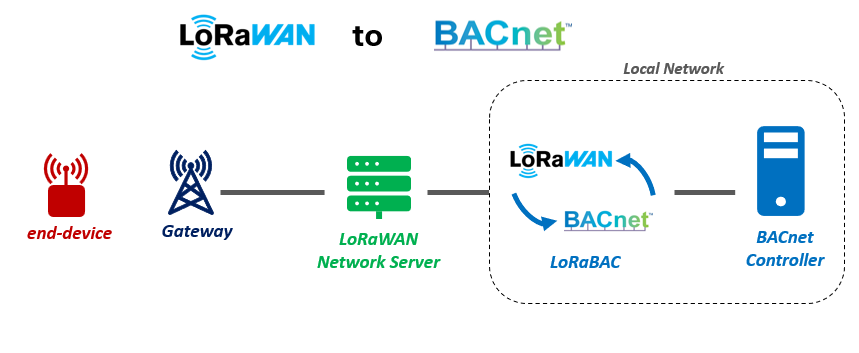
Key Features:
Universal Compatibility:
- Works with all LoRaWAN end-devices and gateways.
- Supports ChirpStack, Actility, and The Things Stack (The Things Network / The Things Industries) Network Servers.
- Integrates with all BACnet controllers using native BACnet protocols (or Distech-Controls controllers when using Rest API).
Bidirectional Communication:
- Uplink: Writes LoRaWAN payloads to specific BACnet objects.
- Downlink: Writes BACnet objects to specific LoRaWAN payload.
Proven Use Cases:
- Thermostatic valves
- Temperature and humidity sensors
- Air quality sensors
- Current monitoring sensors
- Pilot wired electric heater controller
1.2. What Makes LoRaBAC Unique?
LoRaBAC is designed with a different approach compared to other LoRaWAN-BACnet interfaces. Here’s why it stands out:
Advantages :
BACnet Client Architecture:
- Unlike most interfaces that act as BACnet servers, LoRaBAC operates as a BACnet client. It only interacts with the controller when a LoRaWAN payload is received, reducing unnecessary traffic.
Flexible Deployment:
- LoRaBAC can be installed anywhere:
- On the LoRaWAN Gateway
- Within the local network
- Directly on the BACnet controller
- LoRaBAC can be installed anywhere:
Open Source and Free:
- LoRaBAC is free to use and open-source under the MIT License, offering full transparency and customization.
Drawbacks:
No "Who-is" Service Support:
- LoRaBAC does not respond to the "Who-is" service, which can be useful for discovering BACnet devices in some setups.
Manual Configuration Required:
- Each new LoRaWAN device type requires manual configuration. It is not a "Plug and Play" solution.
1.3. Support
To get support on LoRaWAN or LoRaBAC, please refers to the following ressources, or reach us out.
:tv: Webinar Replay: LoRaWAN and BACnet interfaces for Smart Building
:notebook: Free ebook:LoRaWAN for beginers books
:tv: E-learning platform: LoRaWAN for beginers videos
:tv: E-learning platform for Advanced users: LoRaWAN for Advanced users videos
:bulb: 2 days training sessions: LoRaWAN and IoT Training
2. Prerequisites
2.1. LoRaWAN End-Device
To use LoRaBAC you will need:
- a LoRaWAN Network Server (ChirpStack, TTN or Actility).
- The device payload decoders (for uplink).
- the device payload encoders (for downlink, if needed).
Payload decoder and encoders should be provided by your device manufacturer, however, in this repository you will find the payload codec of the tested devices.
2.2. MQTT Broker
LoRaBAC relies on an MQTT broker for communication. You can use:
- The built-in MQTT broker provided by ChirpStack, Actility, or The Things Stack.
- Your own custom MQTT broker.
2.3. Node-RED Setup
LoRaBAC is a Node-RED flow, so you need a Node-RED instance to run it. Ensure the following packages are installed:
- @montagny/node-red-contrib-lorawan-bacnet
Additional Packages for ChirpStackV4:
If you’re using ChirpStackV4 and want to enable the "Flush Downlink Queue" feature, install:
@grpc/grpc-js@chirpstack/chirpstack-api
Quick Start with Docker:
A pre-configured Node-RED Docker image is available on Docker Hub. It includes all required packages for easy deployment.
3. Getting Started
Please, follow the information given in the LoRaBAC application.
