@chart-sg/node-red-ros2 1.0.0
ROS2 nodes for Node-RED with SharedManager architecture. Eliminates conflicts and enables reliable multi-plugin compatibility.
@chart-sg/node-red-ros2
A Node-RED package providing ROS2 integration with seamless multi-plugin compatibility through the Chart SharedManager architecture.
Key Improvements
- Manager Integration: Built-in
@chart-sg/node-red-ros2-managerfor seamless multi-plugin compatibility - Async Initialization: Robust async patterns with proper error handling
- Hot Redeployment: Proper cleanup and re-initialization support
- Multi-Plugin Compatible: Works alongside
@chart-sg/node-red-rmfand other Chart ROS2 plugins - ActionClient Reliability: No spinning conflicts or nullptr errors
Installation
# 1. Source ROS2 environment
source /opt/ros/jazzy/setup.bash # (or your ROS2 distro)
# 2. Install in Node-RED directory
cd ~/.node-red
npm install rclnodejs
npm install @chart-sg/node-red-ros2
The @chart-sg/node-red-ros2-manager dependency is automatically installed.
Architecture
This package uses the Chart SharedManager architecture:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ @chart-sg/node-red-ros2-manager │
│ (Shared ROS2 Context Manager) │
└─────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────────────┘
│
┌───────────┴──────────┐
│ │
┌─────────▼──────────┐ ┌────────▼─────────┐
│ @chart-sg/node- │ │ @chart-sg/node- │
│ red-ros2 │ │ red-rmf │
└────────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘
Benefits:
- No ROS2 context conflicts between plugins
- Shared spinning coordination - efficient resource usage
- ActionClient reliability - no spinning conflicts or nullptr errors
- Automatic lifecycle management - proper cleanup during redeployments
Usage
All nodes automatically use the SharedManager for reliable ROS2 operations:
// Nodes automatically use SharedManager (always available)
const manager = require('@chart-sg/node-red-ros2-manager');
await manager.initialize();
const {node, nodeId} = await manager.createNode('my_node');
Compatibility
- SharedManager Integration: Guaranteed multi-plugin compatibility with shared ROS2 context
- Node-RED: Hot deployment, proper cleanup, lifecycle management
- Multi-Plugin: Works seamlessly with
@chart-sg/node-red-rmfand other Chart ROS2 plugins
Available Nodes
- Publisher - Publish ROS2 messages
- Subscriber - Subscribe to ROS2 topics
- Service Client - Call ROS2 services
- Action Client - Execute ROS2 actions
- ROS2 Types - Message type definitions
- DDS Settings - Configure DDS parameters
🔗 Related Packages
@chart-sg/node-red-ros2-manager- Shared ROS2 context manager@chart-sg/node-red-rmf- RMF integration for Node-RED
Node-RED palette
The main concepts associated with Node-RED operation are explained here. The plugin nodes are displayed on the Node-RED palette as shown in the image. From there, they can be dragged into the flow workspace.
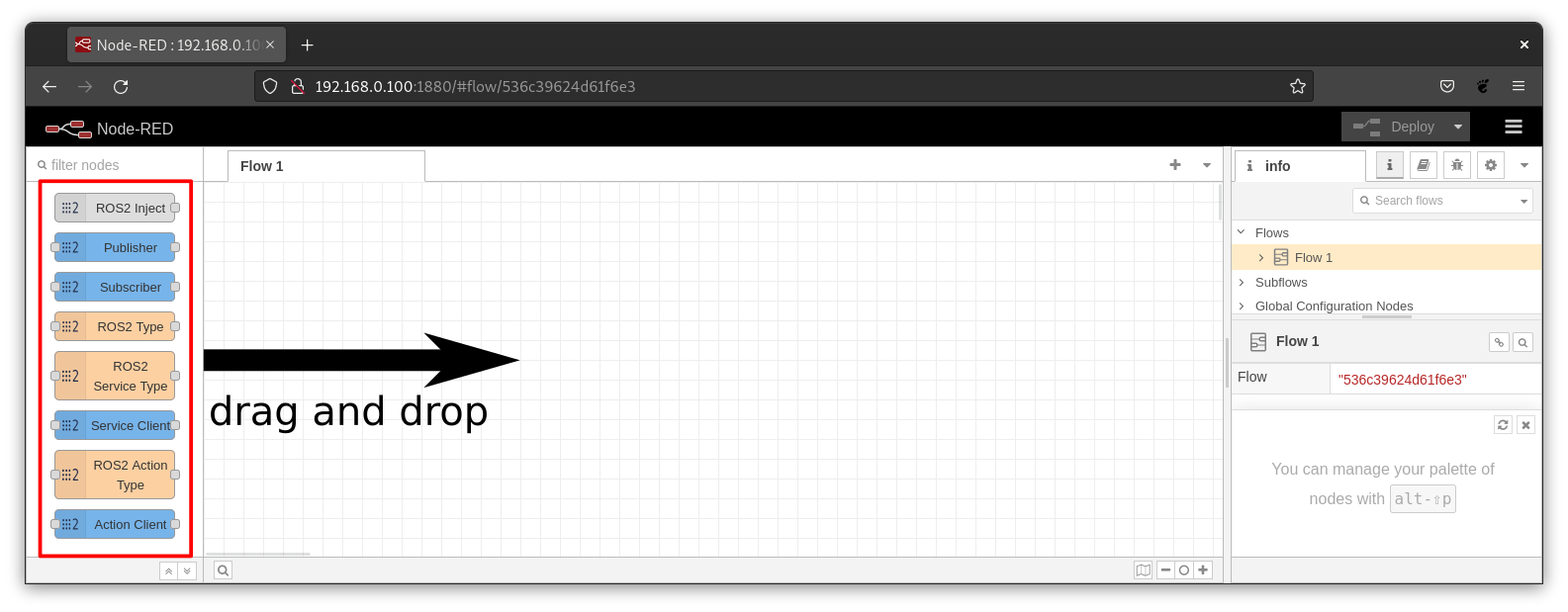
These palette represents the basic ROS client features like publishing and subscribing to a ROS topic, requesting an ROS service or performing a ROS action. With this features it should be possible to control existing ROS system like a robot and to use higher level application like the Nav2 (Navigation Stack).
Note : the text that labels the node, changes from palette to workspace, and may change depending on the node configuration.
Publishing and Subscribing to an ROS Topic
In order the publish or subscribe data we need first to specify the associated type. The topic type is represented by the node ROS2 Type. It is required that the ROS2 Type is connected to the Publisher or Subscriber Node.
Choosing a ROS2 type
 |
This node represents a specific ROS2 Types installed on the system. Once in the workspace, its set up dialog can be opened by double clicking over it. |
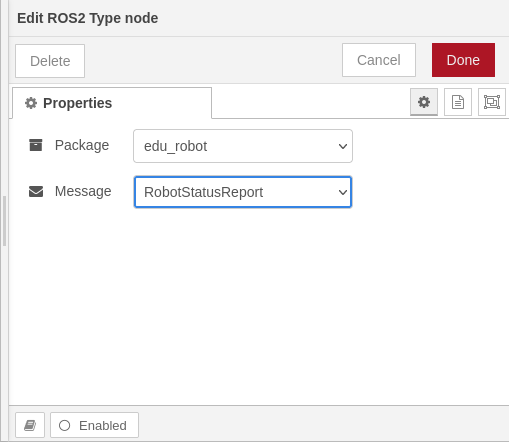 |
The dialog provides a Package drop-down control where all ROS2 msg packages are listed. Once a package is selected the Message drop-down control allows selection of a package specific message. In this example the package selected is edu_robot. From this package the RobotStatusReport message is selected. |
 |
Once the dialog set up is saved, the node label changes to highlight the selected type in a package/message pattern. |
Injecting a type instance into the pipeline
Node-RED pipelines start in source nodes. The most popular one is the inject node which requires the user to manually defined each field associated to the type. In order to simplify this a specific node is introduced:

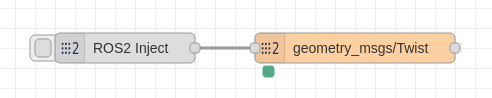
This node mimics the inject node behaviour but automatically populates the input dialog with the fields associated with any type node linked to it. For example, if we wire together a ROS2 Inject and a ROS2 Type as shown in the figure:
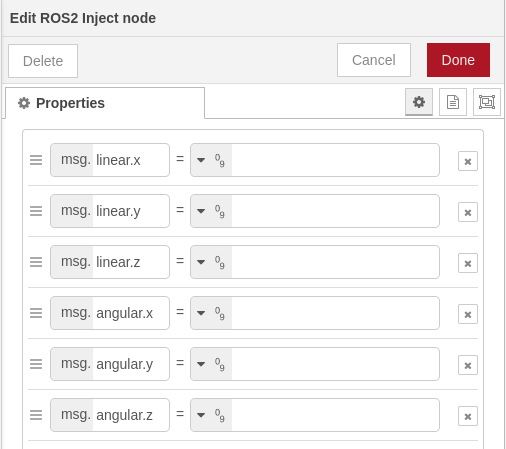
The associated dialogs are populated with the linked type fields and types. For example the twist message is populated as:
ROS2 nodes: General Settings
In order to interact with a ROS2 environment we must specify the same domain id in use for that environment.
The domain id is a number in the range [0, 166] that provides isolation for ROS2 nodes.
It defaults to 0 and its main advantage is reduce the incomming traffic for each ROS2 node, discharging them and
speeding things up.
Another key concepts in the ROS2 environment are:
- topic one. A topic is a text string ROS2 nodes use to notify all other nodes in which data they are interested. When a ROS2 node wants to send or receive data it must specify:
- Which type is the data they want receive. For example the
edu_robot/RobotStatusReportwe introduced above. - Topic associated with the data. For example
/status_report, but in ROS2 topics are often decorated using namespaces to simplify identification, as in/eduard/red/status_report.
- Quality of Service (QoS). Those are
policies that allow fine tunning of the communication between nodes. For example:
- History QoS allows to discard messages if only the most recent one is meaningful for our purposes.
- Reliable QoS enforces message reception by resending it until the receiver acknowledges it.
- Durability QoS assures messages published before the receiver node creation would be delivered.
Note: ROS2 nodes can only communicate if their respective QoS are compatible. Information on QoS compatibility is available here.
ROS2 Subscriber
 |
This node represents a ROS2 subscriber. It is able to subscribe on a specific topic and receive all messages published for it. |
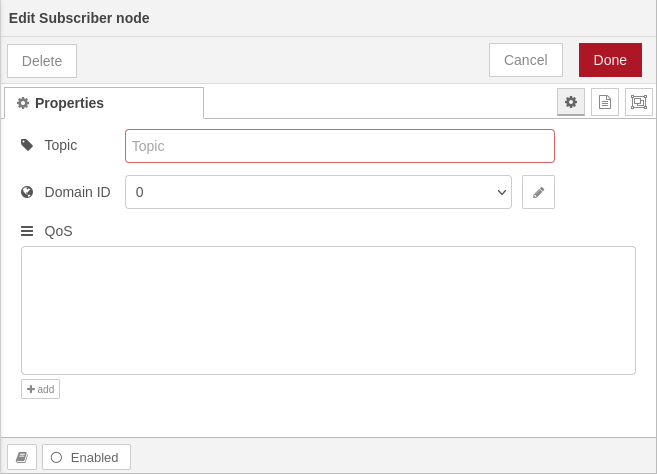 |
The dialog provides controls to configure:
|
Example
This example shows how to subscribe to an topic and display it using the debug node. It is based on the available topics of an EduArt's robot like Eduard.
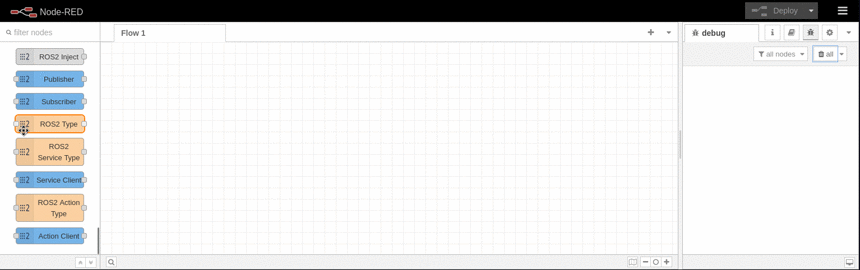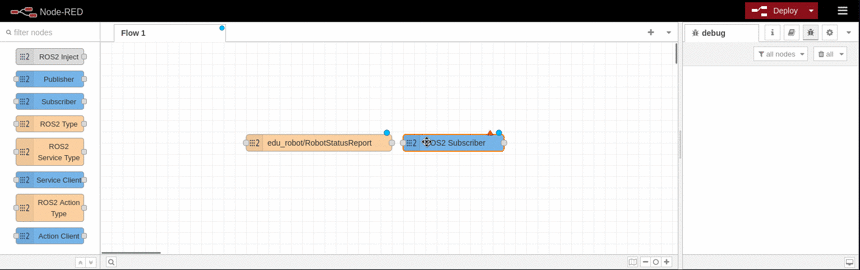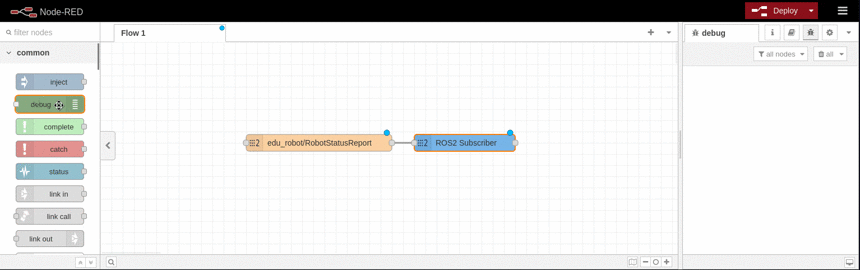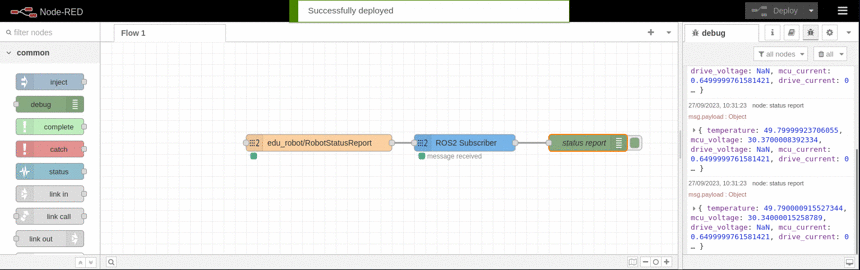
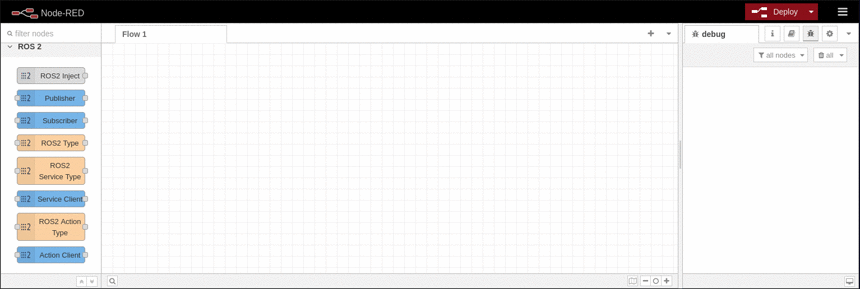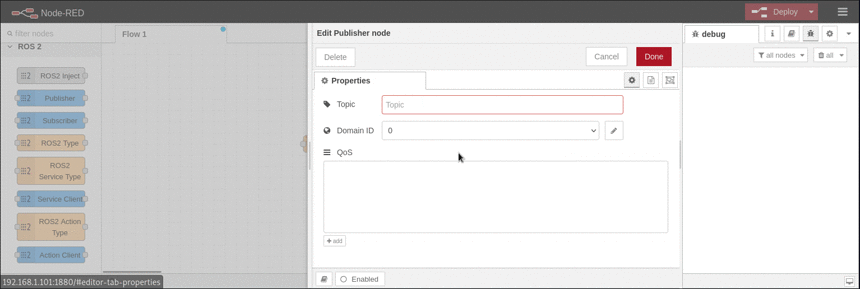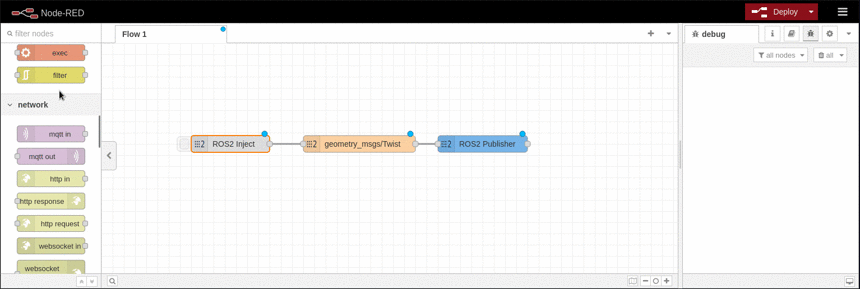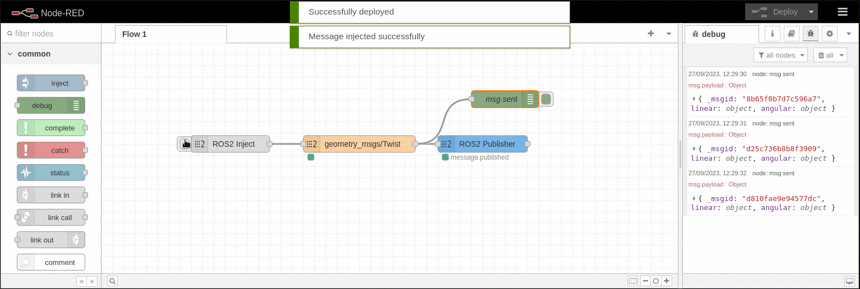
ROS2 Publisher
 |
This node represents a ROS2 publisher. It is able to publish messages on a specific topic with specific QoS |
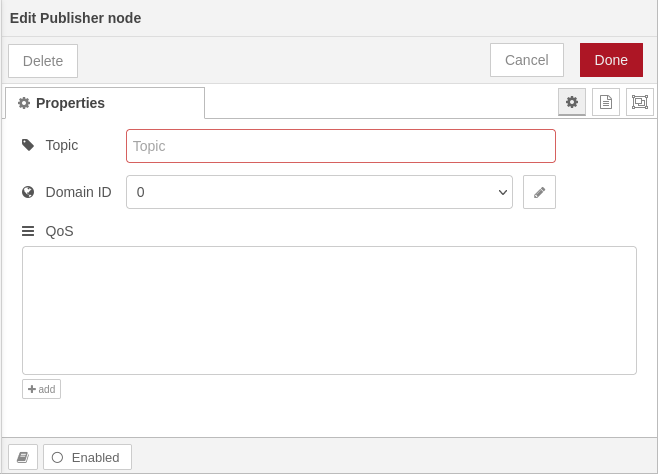 |
The dialog provides controls to configure:
|
Example
This example shows how to publish to an topic and display the published message using the debug node. It is based on the available topics of an EduArt's robot like Eduard.
ROS2 Service Client
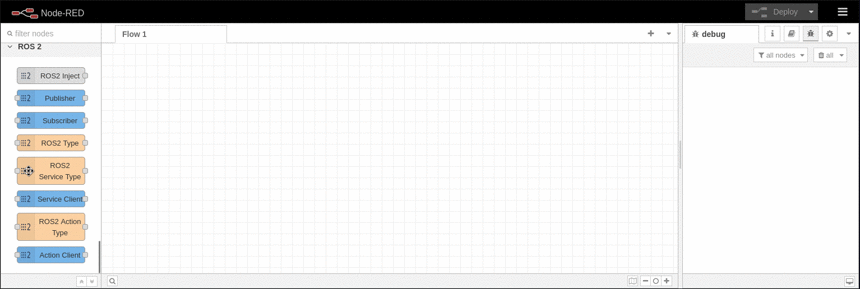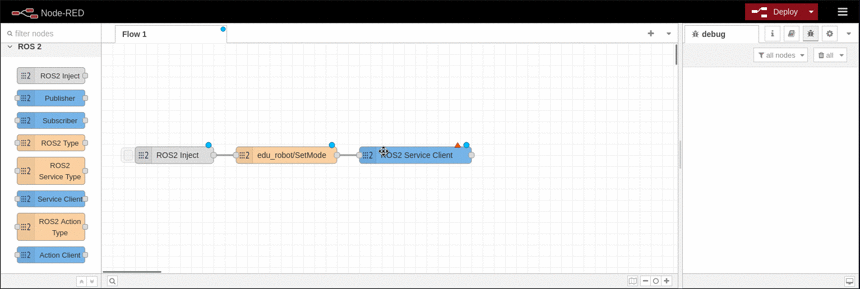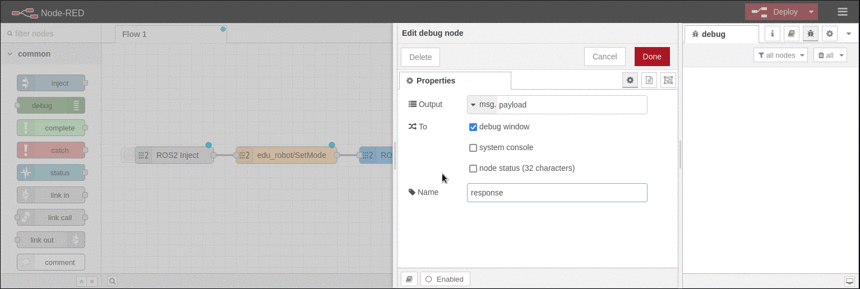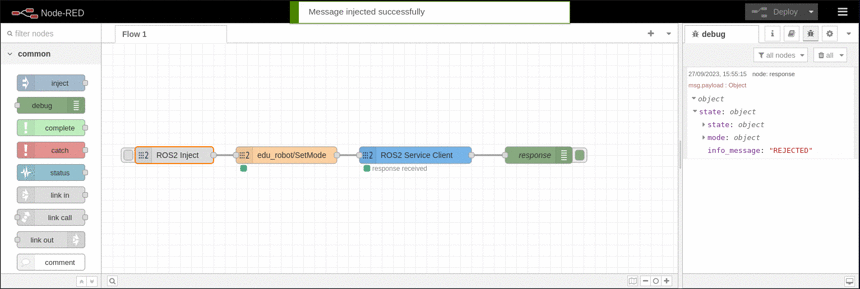
In order to call or request an ROS service we need first to specify the associated type. The service type is represented by the node ROS2 Service Type. It is required that the ROS2 Service Type is connected to the Service Client node.
 |
This node represents a ROS2 service client. It is able to call a specific service with specific QoS. The connected injection injects the service request only. After a successful service call the service response is output. |
 |
The dialog provides controls to configure:
|
Example
This example shows how to call a service and displays the response using a debug node. It is based on the available topics of an EduArt's robot like Eduard. In this example the robot is switched in mode autonomous drive.
ROS2 Action Client
In order to perform a ROS action we need first to specify the associated type. The action type is represented by the node ROS2 Action Type. It is required that the ROS2 Action Type is connected to the Action Client node.
 |
This node represents a ROS2 action client. It is able to perform a specific action with specific QoS. The connected injection injects the action goal request only. After a accepted action goal the action feedback and the final result is outputted. |
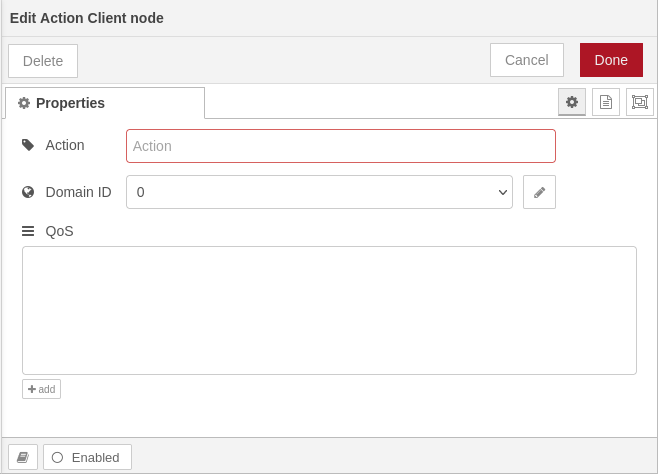 |
The dialog provides controls to configure:
|
Original Project
This fork is based on edu-nodered-ros2-plugin by EduArt Robotik.
📄 License
ISC License - see LICENSE file for details.
